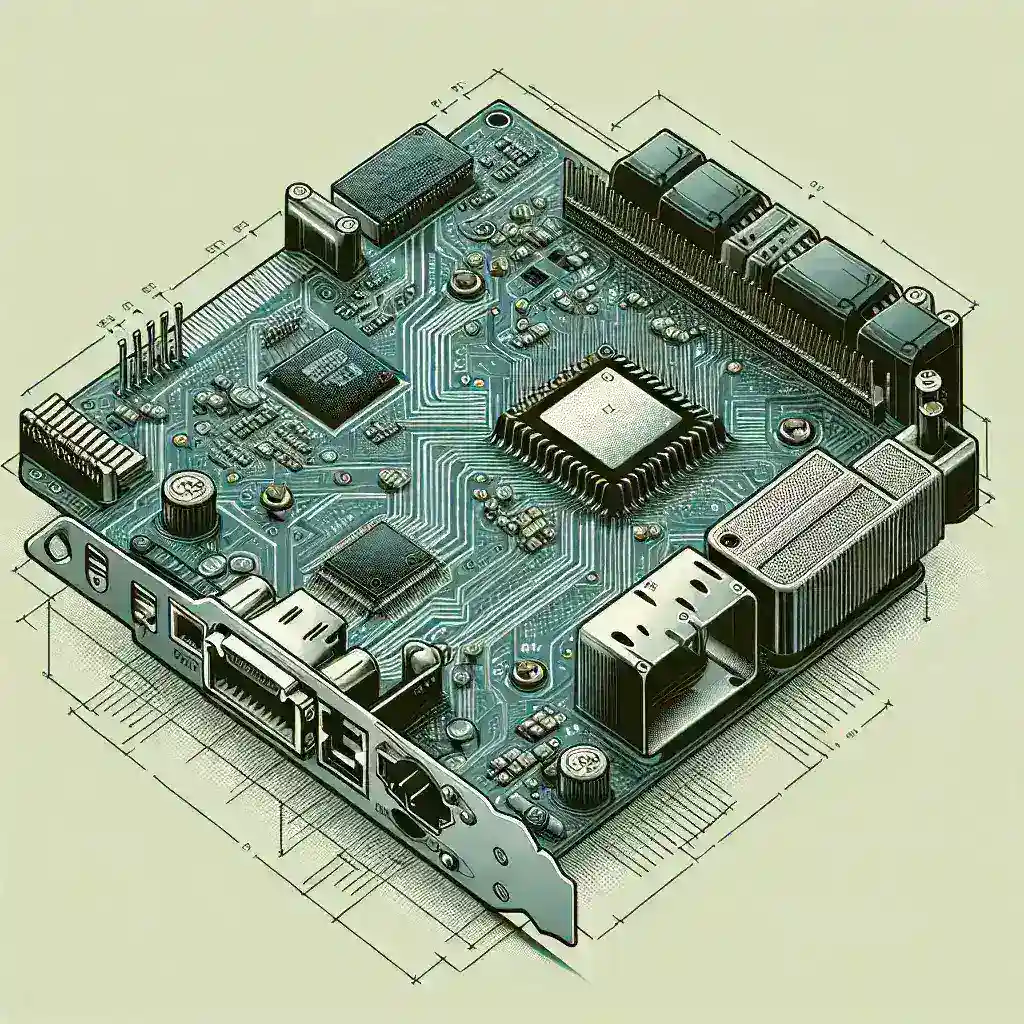
Introduction to Network Interface Card (NIC)
A Network Interface Card (NIC) is an essential hardware component that allows computers and other devices to connect to a network. Whether it’s for a local area network (LAN) or a larger-scale wide area network (WAN), the NIC plays a crucial role in facilitating communication and data exchange between connected devices.
Types of NIC
NICs come in various forms and designs to accommodate different network needs. The two primary types of NICs are:
- Ethernet NIC: The most common type, typically found in desktops and laptops, designed to connect devices via Ethernet cables.
- Wireless NIC: Also known as WiFi cards, these connect devices to wireless networks.
Key Functions of a NIC
The Network Interface Card serves several important functions that enable smooth network operations:
- Signal Conversion: Converts data from parallel to serial form (and vice versa).
- Data Transmission: Sends and receives data packets over the network.
- Error Detection: Identifies and corrects errors in transmitted data.
- Addressing: Assigns unique MAC addresses to each networked device.
Understanding NIC Components
A NIC comprises several critical components, each responsible for specific tasks:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| MAC (Media Access Control) Address | Unique identifier for each NIC |
| Interface | Connection point for network cables |
| Transceiver | Converts signals to appropriate form |
| Buffer | Temporary storage for data packets |
| Driver | Software that controls the NIC |
Types of Network Adapters
Depending on the network requirements, different types of NICs can be employed:
- PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) NIC: Installed on motherboard slots, common in desktops.
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) NIC: Portable NICs that connect via USB ports, ideal for laptops.
- PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) NIC: An advanced version of PCI, offering higher speed and efficiency.
- PCMCIA (Personal Computer Memory Card International Association) NIC: For older laptops with PC Card slots.
Advantages of Using a NIC
Implementing a Network Interface Card brings numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Connectivity: Facilitates reliable network connections.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: Enables fast data transmission.
- Improved Performance: Offers stable and efficient network performance.
- Cost-Effective: Widely available and affordable.
How NICs Contribute to Network Performance
NICs significantly impact overall network performance by:
- Minimizing Latency: Reducing delay in data transmission.
- Boosting Bandwidth: Increasing available network bandwidth for faster connections.
- Ensuring Reliability: Maintaining stable connections even in high-traffic scenarios.
Choosing the Right NIC
When selecting a Network Interface Card, consider factors such as:
- Network Type: Determine if you need an Ethernet or wireless connection.
- Speed and Compatibility: Ensure the NIC supports your device and desired network speed.
- Port Availability: Check the number of ports for connecting multiple devices.
- Price: Budget-friendly options without compromising quality.
Conclusion
Network Interface Cards are integral to modern networking, bridging the gap between computers and networks. Whether you need a wired or wireless connection, understanding the types, functions, and benefits of NICs can help you make informed decisions to enhance your network’s efficiency and performance.